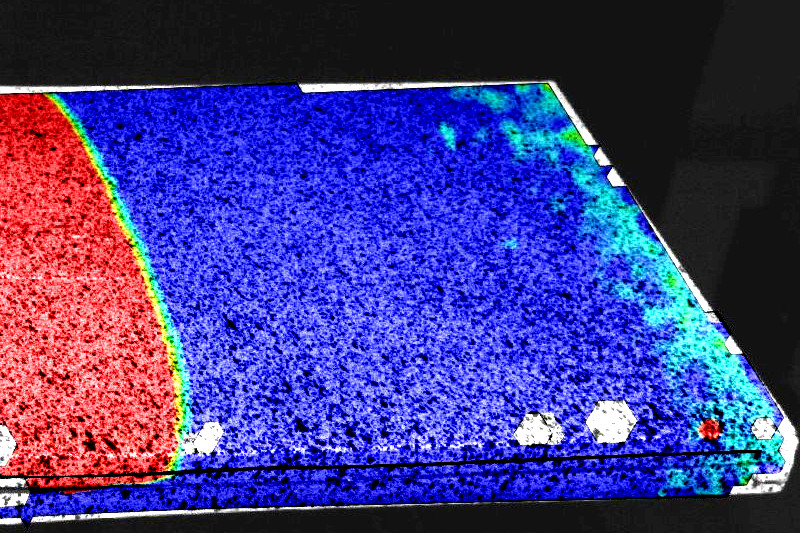
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) technology allows us to precisely measure the deformations of the sample over time by comparing a series of photos taken during the experiment. In this example, the tearing of the glued joint between two aluminum plates is monitored and DIC technology allows us to actually see what is happening under the surface of the aluminum. The part where the glue is undamaged is marked in blue, the part where the glue is damaged is red. The front of the crack in the adhesive with a zone of partial damage is marked in other shades.